Normal 2d measurements from the apical 4 chamber view.
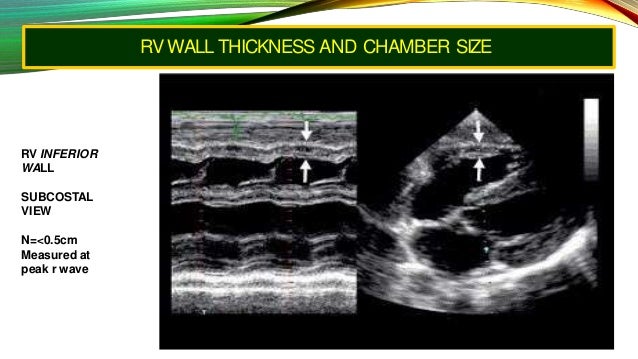
Normal rv wall thickness.
Rv wall thickness m mode or 2d.
Here we retrospectively evaluate the thickness of the inferior rv wall irvwt by echo in neonates and infants with normal.
How does acute rv enlargement differ from chronic rv enlargement.
Normal is less than 5 mm best is ps la second is subcostal.
An established echocardiographic echo standard for assessing the newborn right ventricle rv for hypertrophy has not been thoroughly developed.
Normal or increased thickness is expected in chronic rv enlargement.
Rv and or lv dysfunction using the normal cut off of.
Enddiastolic volume of the rv body surface ml m male 35 87 females 32 74.
This is partially due to the rv s complex architecture which makes quantification of rv mass by echo difficult.
Normal range on the basis of a right ventricle appearing significantly larger than the left ventricle.
Enddiastolic area of the rv body surface cm m male 5 12 6 females 4 5 11 5.
Moody jr md uthscsa and almmvah october 2001.
Assessing rv performance.
Rv medio lateral end diastolic dimension 4 3 cm rv end diastolic area 35 5 cm 2 maximal ra medio lateral and supero inferior dimensions 4 6 cm and 4 9 cm respectively maximal ra volume 33 ml m 2 35 89.
Dilatation is more conspicuous in acute rve pulmonary embolism rv infarct associated wall motion defects and thinning favors acute rve.
Endsystolic area of the rv body surface cm m.
Normal 2d measurements from the apical 4 chamber view.
Echo assessment of rv walls weyman 1994 p.
Echo assessment of rv 3 0 2 5 3 8.
Here is a five star rated article on rv dimension.
Assessing rv thickness size and function joe m.
Right ventricular wall thickness mm bis 5 mm.
Rv medio lateral end diastolic dimension 4 3 cm rv end diastolic area 35 5 cm 2 maximal ra medio lateral and supero inferior dimensions 4 6 cm and 4 9 cm respectively maximal ra volume 33 ml m 2 35 89.